Traceroute For Mac Os
You can use the standard ping that the Mac OSX comes with to find pmtu. Ping -D -s shoud do the trick. Please note, the size is just the ICMP datagram payload size. To see the IP MTU, you need to add 8 bytes of the ICMP header and 20 bytes of the IP header (so for example, to send 1500 Bytes long IP packet, you need to specify size as 1472).

Traceroute For Mac Os Catalina
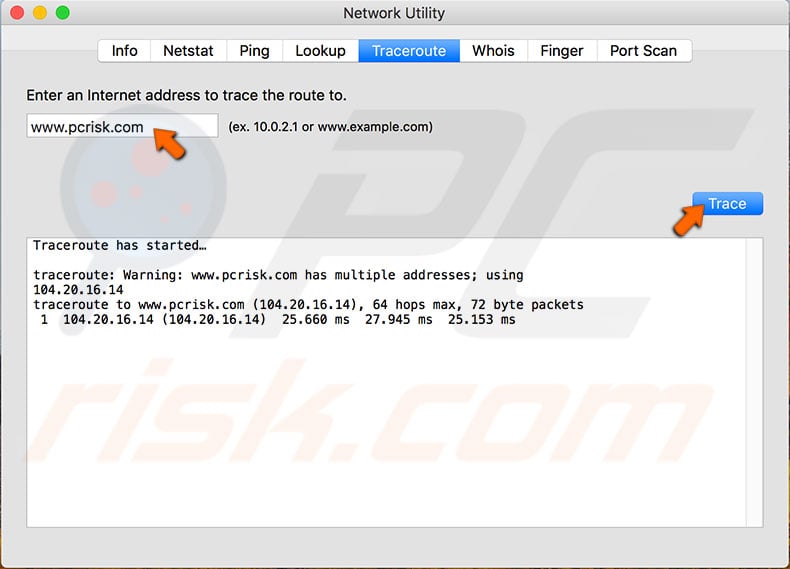
Traceroute allows you to discover a network path from one host to another. Traceroute is extremely helpful examining network hops (or network devices traversed over) and information including IP Address, DNS servers, and average time taken over each hop. A popular use of traceroute is to identify network bottlenecks (poor speed performance) happening in network equipment you do not own (network equipment in the Internet). Use Terminal in Mac OS X to traceroute any network address on your local network or the Internet.
Mac Os Route Command
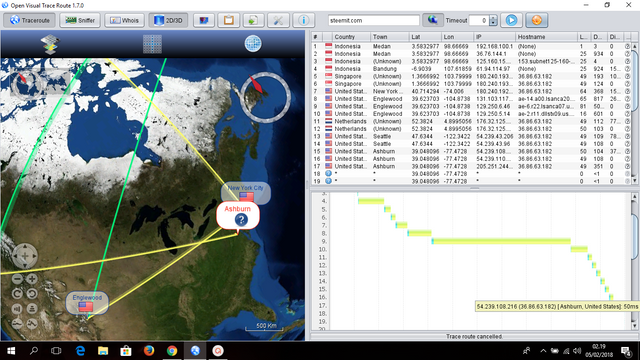
WhatRoute Overview A Network Utility for MacOS X WhatRoute is a network diagnostic utility designed for Apple Macintosh computers. Primarily it provides a Traceroute function, but can also perform Ping, Domain Name Service queries, Whois queries and monitor the traffic to and from your computer. Free download VisualRoute VisualRoute for Mac OS X. VisualRoute - Graphical View of Traceroute provides key data in an easily digestible way. In computing, traceroute and tracert are computer network diagnostic commands for displaying possible routes (paths) and measuring transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The history of the route is recorded as the round-trip times of the packets received from each successive host (remote node) in the route (path); the sum of the mean times in each hop is a measure. VisualRoute for Mac Free to try Visualware Mac OS X 10.3/10.3.9/10.4 Intel/10.4 PPC/10.5 Intel/10.5 PPC/10.6 Intel Version 14.0l Full Specs Editors' Rating.
Note: While traceroute attempts to explore network path hosts typically outside your private network, traceroute results always vary depending on the network hops you attempt to resolve. For instance, you may not receive replies from every device in your traceroute. Unresponsive devices are represented as 3 asterisks ***. Traceroute will always try to resolve hosts, but it can’t always. Devices that it cannot resolve are usually blocked by a firewall.
1. Open Terminal (Applications -> Utilities -> Terminal)
2. Type the following command
3. Terminal will send a network packet to google.com. Watch as the network packet moves out of your local network, past your ISP, and into the wild. Eventually, the traceroute will complete and it should look like something similar below.
As you see, traceroute provides detailed information about a network destination. Traceroute has a variety of command options you can play with in Terminal. Take a look below.

